 The Raspberry Pi has 40 General purpose Input/output Pins (GPIO) that can be used for controlling external hardware.
The Raspberry Pi has 40 General purpose Input/output Pins (GPIO) that can be used for controlling external hardware.
There are a number of add-on boards called hats which plug into these pins and provide various sensors. The most common one being the sense hat.
Although you will need external hardware like leds etc for various projects there is a lot you can learn without using any.
In this tutorial I will cover the basics of using the GPIO pins and show you how to use MQTT to set the pin state and report the pin state using Python..
PIN or Channel Numbers
This aspect I found very confusing at first as there are two systems that are used, and you need to choose which one to use in your scripts.
The systems are:
- Board- uses numbers 1-40 and follows the pin Layout.
- BCM – uses designations line GPIO4
GPIO4 corresponds to Board Pin number 7 as shown in the diagram below: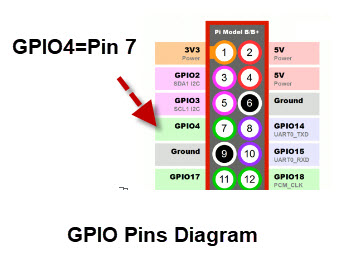
Note: diagram copied from this page which contains complete pin layout
Reference reading:
Simple guide to the Raspberry pi GPIO pins
Controlling The Pins Using Python
There are two modules that can be used for controlling i.e reading and writing to the pins. They are:
- RPI.GPIO – install ref
- gpiozero – install ref
Both modules are normally installed but the install procedures can be found on the reference pages above.
Using
To use you will need to import them. The code is
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
or
import gpiozero
Using The RPI.GPIO Module
To use a pin you need to first set the numbering scheme and then designate the Pin as either an input or an output pin.
Using the BCM format we use:
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) #set numbering scheme GPIO.setup(4,GPIO.OUT) #set GPIO4 as output. GPIO.setoutput(4,1) #set value of GPIO4 to True or 1
to set a pin as an input pin use:
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) #set numbering scheme GPIO.setup(5,GPIO.IN) #set GPIO5 as input.
You can read the value of a pin using:
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) #set numbering scheme GPIO.setup(4,GPIO.OUT) #set GPIO4 as output. GPIO.setoutput(4,1) #set value of GPIO4 to True or 1 GPIO.setup(5,GPIO.IN) #set GPIO5 as input. pin5=GPIO.input(5) #Read value GPIO5. pin4=GPIO.input(4) #Read value GPIO4.
Note: GPIO.BCM,GPIO.OUT etc are constants and pins are often called channels when using the BCM scheme.
Test Script
The following script demonstrates the above:
#! /usr/bin/python3.5
import sys
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
cpio_channels=[4,5,6,12,13,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]# base channels
print("using ",sys.version) #what version of python
mode=GPIO.getmode()
print("mode is ",mode)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
mode=GPIO.getmode()
print("mode is ",mode)
GPIO.setup(4,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(4,1)
print("value is ",GPIO.input(4))
GPIO.setup(5,GPIO.IN)
print("input value is ",GPIO.input(5))
GPIO.cleanup()
print("board ",GPIO.BOARD)
print("bcm ",GPIO.BCM)
Connecting to MQTT
To publish the value of a pin we first need to decide on a topic naming scheme.
To set the value of the pin we also need a control topic.
Below I use:
- pi/GPIO/channel_number
- pi/GPIO/control/channel_number
To publish on pin/channel 4 (GPIO4) we use
#First setup MQTT See later
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) #set numbering scheme
GPIO.setup(4,GPIO.OUT) #set GPIO4 as output.
GPIO.setoutput(4,1) #set value of GPIO4 to True or 1
mqtt.publish("pi/GPIO/4",GPIO.input(4))
Controlling Pins using MQTT
The script below is available as a download and will let you control an output pin/channel using MQTT.
To test I used the mosquitto_pub tool with a payload of 1 or 0
e.g
mosquitto_pub -h 192,168.1.158 -t pi/GPIO/control/4 -m 1
will set the pin/channel to 1.
The script will publish the channel/pin value on
pi/GPIO/4.
So you can subscribe to this topic and see it change as you send the commands.
FeedBack
I created this tutorial as a response to a question I received. I never intended to use the GPIO pins myself. Therefore I would be grateful for any feedback you may have.
Related tutorials and resources:
- Getting started with the MQTT client
- How to Send and Receive JSON Data Over MQTT with Python
- How to Encrypt MQTT Payloads with Python – Example Code
- Send and Receive Integers and Floats with Arduino over MQTT
- Arduino -Sending and Receiving JSON Data over MQTT
- Using the Arduino PubSub MQTT Client


I now have a ‘case’ statement as a ‘while’ loop containing some nested ‘if’ bits of code. Each if statement will do something to a couple of GPIO pins.. How do I do:
if(word sent by MQTT)
GPIO.output(4, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(6, GPIO.HIGH)
elseif (Word2 sent by MQTT)
do another thing
Sorry if my python is not quite right, I’m not checking it.
Is it along the lines of
if( MQTTword == ‘forward’)
Thanks for any advice on this. I’m struggling.
Peter M.
Peter if you download the python script you will see I put the incoming message in an array and retrive them in the variable m. m[1] is the actual message. So suing that you would write
if m[1]==”on”:
GPIO.output(4, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(6, GPIO.HIGH)
if if m[1]==”off”:
GPIO.output(4, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(6, GPIO.HIGH)
Does that make sense?
rgds
Steve
Thank you Steve, Very Cool!