 To receive messages on a topic you will need to subscribe to the topic or topics.
To receive messages on a topic you will need to subscribe to the topic or topics.
To subscribe to a topic you use the subscribe method of the Paho MQTT Client Class.
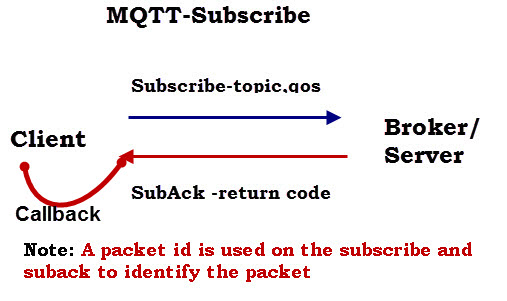
As shown in the diagram above subscribe messages are acknowledged by a SubAck message.
To subscribe you need to supply
- QOS -0,1,2
- Topic or topics
You should note that you can subscribe to multiple topics with one function call.
We can also send subscribe properties when using MQTT v5.
Again as with the publish message we need to listen on the packetreceive event to get the SubAck message.
The Subscribe API
First you create a client object and then call the subscribe method as below:
client.subscribe(topic/topic array/topic object, [options], [callback])
You can pass a single topic and array of topics and a topic object.
Options are:
- QOS -0,1,2
- Topic or topics
- No Local -MQTT v5
- Retain as Published -MQTT v5
- Retain Handling -MQTT v5
- Properties -MQTT v5
The callback function has the form shown below:
function (err, granted)
where:
err a subscription error or an error that occurs when client is disconnecting
granted is an array of {topic, qos} where:
topic is a subscribed to topic
qos is the granted QoS level on it
Events
To capture the SubAck we need to listen to the packetreceive event as shown below:
client.on("packetreceive",function(packet){
console.log("receive packet "+ JSON.stringify(packet));
})
This is what we see:
connected true
subscribing to topics
receive packet {"cmd":"suback","retain":false,"qos":0,"dup":false,"length":3,"topic":null,"payload":null,"granted":[1],"messageId":26988}
Timing
Because node.js uses asynchronous functions you need to be careful with timings.
For example the process
- connect
- subscribe
May not work because the subscribe occurs before the connection is complete. In other languages we simply wait for the connection to complete like this:
- connect
- wait for connection
- publish
but in node.js we cannot do this.
If we test for the connection to be established before we subscribe using:
if (client.connected==true){
client.subscribe("testtopic",options)
}
Therefore we almost always subscribe in the on_connect callback.
This way you know that you are connected before you subscribe and it will renew the subscription if the connection is broken.
client.on("connect",function(){
console.log("connected "+ client.connected);
let topic="test_topic";
let options={qos:1};
client.subscribe(topic,options);
})
Subscribe Examples
Subscribe to Single topic
var topic="testtopic";
var message="test message";
console.log("subscribing to topics");
client.subscribe(topic,{qos:1}); //single topic
Subscribe to Multiple topic
In this case they all use the same QOS.
var topics=["testtopic","testtopic2"];
var message="test message";
console.log("subscribing to topics");
client.subscribe(topics,{qos:1}); //single topic
Subscribe to Multiple topics Using Topic Object
In this case the QOS level used is the one in the topic object which below is 0. The QOS set in the options is ignored.
var topics={"testtopic":{qos:0},"testtopic2":{qos:0}};
var message="test message";
console.log("subscribing to topics");
client.subscribe(topics,{qos:1}); //single topic
Subscribe Using the rh Option
This options tells the broker not to send retained messages on subscribing when set to 2 as in the example. You also need to set the protocol version to 5 when you connect for this to work
var topic="testtopic";
console.log("subscribing to topics");
client.subscribe(topic,{qos:0,rh:2}); //single topic
Subscribe using properties
In this example we set the subscription identifier which can be use for incoming message filtering.
Messages sent to the client by the broker contain the subscription identifier that matches the subscription topic.
In this example the topic we subscribe to is testtopic and the subscription identifier is set to 1.
So messages published to testopic will be sent to the client with a subscription identifier is set to 1
var topic="testtopic";
console.log("subscribing to topics");
let subOptions={qos:0,properties:{subscriptionIdentifier:1}}
client.subscribe(topic,subOptions); //single topic
This is what the client receives, notice the subscription Identifier at the end of the payload..
message is test message
topic is testtopic
packet ={"cmd":"publish","retain":true,"qos":0,"dup":false,"length":26,"topic":"testtopic","payload":{"type":"Buffer","data":[116,101,115,116,32,109,101,115,115,97,103,101]},"properties":{"subscriptionIdentifier":1}}
Related tutorials and resources:
- Publishing MQTT messages Using the Node.js Client
- Connecting to an MQTT Broker Using the Node.js Client
- How MQTT Works -Beginners Guide
- MQTT Publish and Subscribe Beginners Guide
